Type of mobile threat: Device
Disable network radios like Bluetooth, NFC, Wi-Fi, and GPS when not in use to minimize attack opportunities. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks whenever feasible due to their potential insecurity. Here are easy measures to secure your networks encompassing wireless and remote access.
- Firewalls that prevent unauthorized access to mobile devices or networks.
Using mobile VPNs is an effective defense against mobile security threats. Check our guide to the best mobile VPNs tailored to your business and personal security needs.
To mitigate risks, employ robust authentication methods, encrypt your device, activate remote tracking and wiping features, refrain from storing sensitive data directly on your device, and stay cautious when handling personal information.
Before opening email attachments or clicking on links, always verify the email’s legitimacy. Phishing emails often impersonate legitimate services or companies to trick you into sharing sensitive data. Be wary, especially of emails in junk or spam folders. Here are ways to prevent phishing attacks.
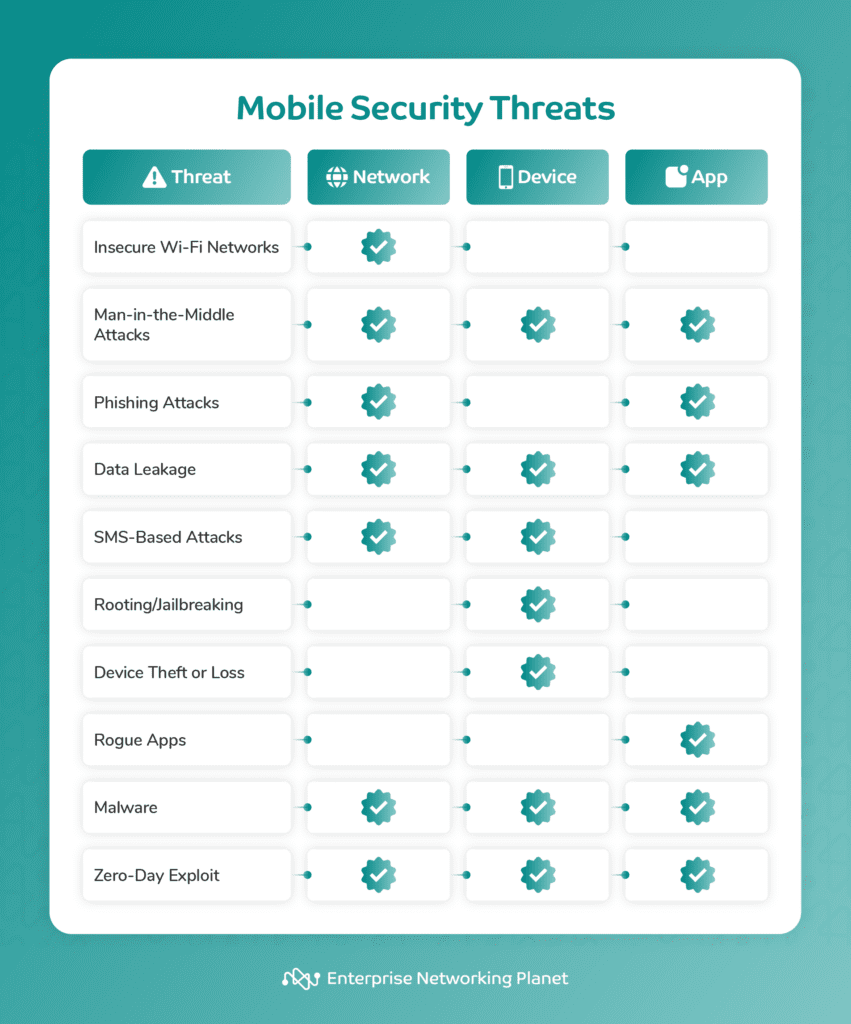
Insecure Wi-Fi networks are vulnerable to exploitation, allowing attackers to intercept data transmissions and gain unauthorized access. Cybercriminals employ tactics like eavesdropping or setting up rogue Wi-Fi hotspots to illegally access systems, launch MITM attacks, or intercept the transmission of sensitive data.
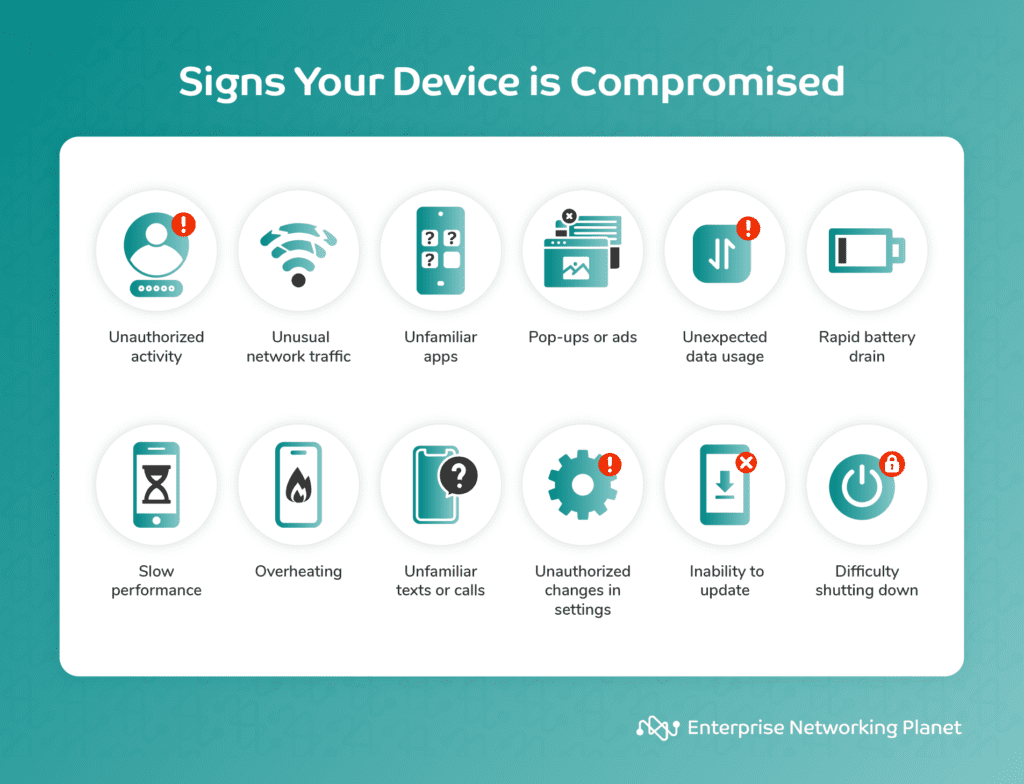
Watch out for signs of device compromise such as unusual activities, network traffic, unfamiliar apps, pop-ups, data usage, battery drain, device sluggishness, overheating, unexpected calls or texts, setting changes, update failures, or difficulty powering down.
MITM attacks involve intercepting and monitoring communication between two parties without their knowledge, achieved through packet sniffing, DNS spoofing, or setting up untrustworthy Wi-Fi hotspots. This grants attackers unauthorized access to sensitive information, endangering user privacy and security.
While primarily a network threat, MITM attacks also expose sensitive data stored on devices connected to compromised networks. In terms of apps, cybercriminals could intercept communication between apps and a server over an insecure network, accessing confidential information or injecting malicious data.
- Mobile threat defense (MTD) to actively defend against mobile threats originating from apps, networks, or devices.
Application-related data leakage occurs when apps unintentionally reveal sensitive data due to coding errors or inadequate security controls.
Type of mobile threat: Device and network
Monitor the personal data apps access. Disable third-party app stores and implement security technology to segregate enterprise data, as recommended by CISA.
Here’s a rundown of the top 10 mobile security threats and what they specifically target: networks, devices, or applications.
At the network level, data leakage can occur if unauthorized individuals access private information transmitted over the network due to weak security protocols or compromised network devices.
Deploying security software on your mobile device can boost protection against malware and enhance overall network security. Mobile security software encompasses:
Stay vigilant against SMS messages from unknown senders requesting personal information, avoid clicking on links from unfamiliar sources, and utilize mobile security apps capable of detecting and blocking malicious content.
Mobile app security threats encompass rogue apps, malware, and zero-day exploits, with overlaps across multiple threat types.
Use encrypted connections like HTTPS, avoid accessing sensitive data on public networks, consider employing a mobile VPN for enhanced security, keep devices and apps up to date, and remain vigilant for any unexpected changes in device or app behavior.
Mobile security threats are pervasive and often more insidious than traditional computer threats. Stay informed, proactive, and vigilant to protect your mobile networks, devices, and apps against the majority of threats and attacks.
SMS-based attacks exploit weaknesses in SMS to deliver malware or phishing links, posing a threat to device security. Attackers send deceptive SMS messages containing malicious links or instructions to trick users into taking actions that could lead to phishing or malware installation, potentially compromising device security.
- Mobile device management (MDM) offers centralized control over mobile devices to enforce security policies, manage settings, and monitor usage safeguarding corporate data integrity.
Prevent rogue app installation by solely downloading apps from official app stores, scrutinize app permissions before installation, maintain updated mobile OS, and use reputable mobile security apps.
To strengthen security, avoid rooting or jailbreaking your device, keep device software updated, and exclusively download apps from trusted official sources.
For more info, visit Lookout.
Download apps exclusively from official stores, as third-party stores may lack security measures. Regularly review and remove unused apps to minimize potential security risks.
Unauthorized data access can occur if your mobile device is lost or stolen, particularly if it lacks adequate security measures like strong passwords or biometric authentication.
- Mobile application management (MAM) overseeing mobile apps and data, managing app lifecycles for secure mobile environments.
Before sharing personal data, verify the legitimacy of websites and apps, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your mobile device for heightened security, and ensure everyone in your organization is educated about phishing attacks and other social engineering threats.
Malware typically infiltrates devices when users accidentally download malicious apps, access insecure websites, or open infected attachments, disrupting device functionality, stealing sensitive information, or enabling unauthorized tracking of user activities.
Type of mobile threat: Network and app
Rogue apps are fake mobile applications commonly used in mobile network hacking. These malicious apps imitate trusted applications to steal sensitive data such as login credentials or bank details, install malware, spyware, or ransomware on the device.
Zero-day exploits present significant risks by exploiting unknown vulnerabilities in software or apps before vendors can release patches. These threats can be utilized across networks to breach defenses, on devices to bypass security layers, or within apps to exploit unpatched flaws.
- Antivirus and anti-malware software that identifies and removes malware from mobile devices.
Strong passwords, PINs, and biometric authentication such as fingerprint or facial recognition can enhance device security against unauthorized access. Utilize 2FA or MFA for additional security where multiple verifications beyond passwords are required.
Protect your device with reputable antivirus and anti-malware software, update mobile OS and apps regularly, and download apps from official stores.
Malware can spread across networks, impacting operations or jeopardizing data transmission, and infiltrate individual devices, weakening security and leading to data theft. Apps can also be targeted by malware exploiting vulnerabilities in their code, illicitly accessing stored or processed data.
- Mobile identity management (MIM) authenticates and authorizes mobile users and devices.
- Mobile VPNs that encrypt and protect mobile data traffic over public networks.
If your device is compromised, take action to rectify the situation, including isolating the device, running security scans, removing malicious apps, updating OS, changing passwords, setting up 2FA or MFA, monitoring account activity, backing up data, installing security apps, resetting to factory settings, seeking expert help, educating yourself and your team.
Type of mobile threat: Network
Phishing attacks involve deceiving individuals into divulging sensitive information through fraudulent apps or messages impersonating legitimate sources. These solicit passwords, credit card details, or other confidential data.
Device data leakage happens when attackers access confidential data stored on devices via malware, physical theft, or weak mobile security settings.
Type of mobile threat: App, device, and network
To combat data leakage, regularly review and manage app permissions, use encrypted connections on public networks, and exercise caution when sharing sensitive information on unsecured platforms.
Type of mobile threat: Device
To enhance security, make sure to use secure, password-protected Wi-Fi networks, enable WPA3 encryption, and utilize a virtual private network (VPN) for an added layer of security when connecting to public Wi-Fi.
Malware is a versatile threat that exploits vulnerabilities at various levels, manifesting as viruses, worms, Trojan horses, or spyware, and undermining mobile device security.
Type of mobile threat: Network, device, and app
Type of mobile threat: App, device, and network
- Mobile content management (MCM), which secures mobile content like documents, images, and videos.
Always update software and apps, leverage security software to mitigate threats, and adhere to vendor security advisories for timely patches.
Implementing security measures like keeping software updated, using strong authentication, maintaining good app security, securing network communications, installing security software, and being cautious of phishing is crucial in defending against mobile threats.
Mobile device security threats include SMS-based attacks, rooting or jailbreaking, and device theft and loss, some of which may overlap between categories.
Content and product recommendations from Enterprise Networking Planet are all independently selected by our editorial team. Clicking on links to our partners may result in us earning a commission. Find out more.
Regular updates for your device’s OS and apps are essential for security maintenance, as updates typically include security patches for vulnerabilities discovered post previous software releases. Enable automatic software updates whenever possible to ensure swift installation.
SMS-based attacks mainly target individual devices to steal sensitive data, send premium-rate SMS messages without consent, or engage in other malicious activities. Additionally, these attacks can be used to conduct Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks on networks, overwhelming a target’s network or device by sending a large volume of SMS messages.
Type of mobile threat: Network, device, and app
Rooting (Android) or jailbreaking (iOS) involves bypassing device restrictions imposed by manufacturers, compromising the device’s security model. While some users root or jailbreak their devices to gain additional control, this practice weakens security, increasing vulnerability to malware and unauthorized access.
Lookout’s Mobile Endpoint Security solution utilizes artificial intelligence and threat intelligence to detect and respond to mobile threats in real time, including spyware, phishing, and credential theft.
Type of mobile threat: App
Data leakage refers to the unauthorized transmission of sensitive data from an organization to an external recipient, often caused by unencrypted connections or apps with excessive permissions allowing access and sharing of user data without consent. Data leakage exposes personal or corporate information, resulting in privacy breaches.
Understanding the risks posed by mobile security is crucial for both personal users and businesses, especially in today’s landscape where mobile devices are widely used in corporate environments. With these devices often holding sensitive business information and providing access to organizational networks, they become attractive targets for cyber threats that can lead to anything from data breaches to disruptions in operations.
Mobile network security threats encompass insecure Wi-Fi networks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, phishing attacks, and data leakage. Some of these threats fall into multiple categories since they target various components.