TensorFlow, a well-established machine learning framework, offers solid support for distributed training through TensorFlow Distributed. Its efficient scalability across multiple machines and GPUs makes it a top choice for training large-scale deep learning models.
Personally, I lean towards PyTorch due to its intuitive API and my familiarity with it. So, I don’t see any need to switch to something new unnecessarily. When it comes to traditional machine learning workflows, I rely on Dask for its lightweight approach that’s native to Python.
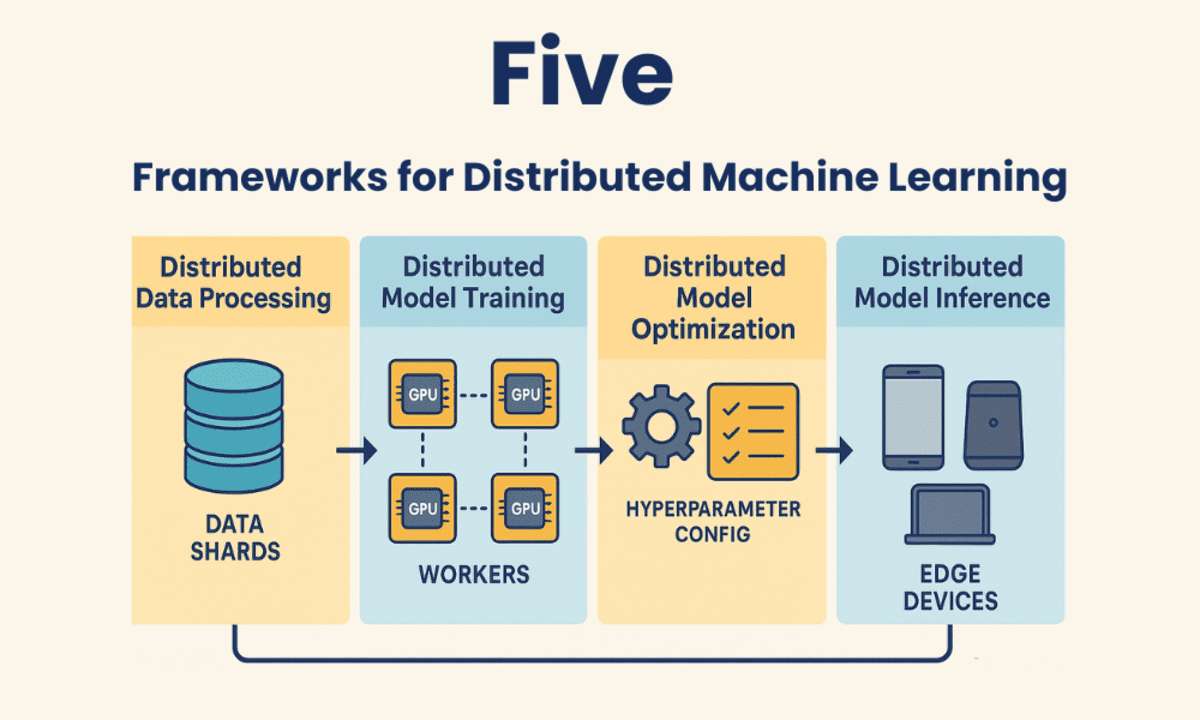
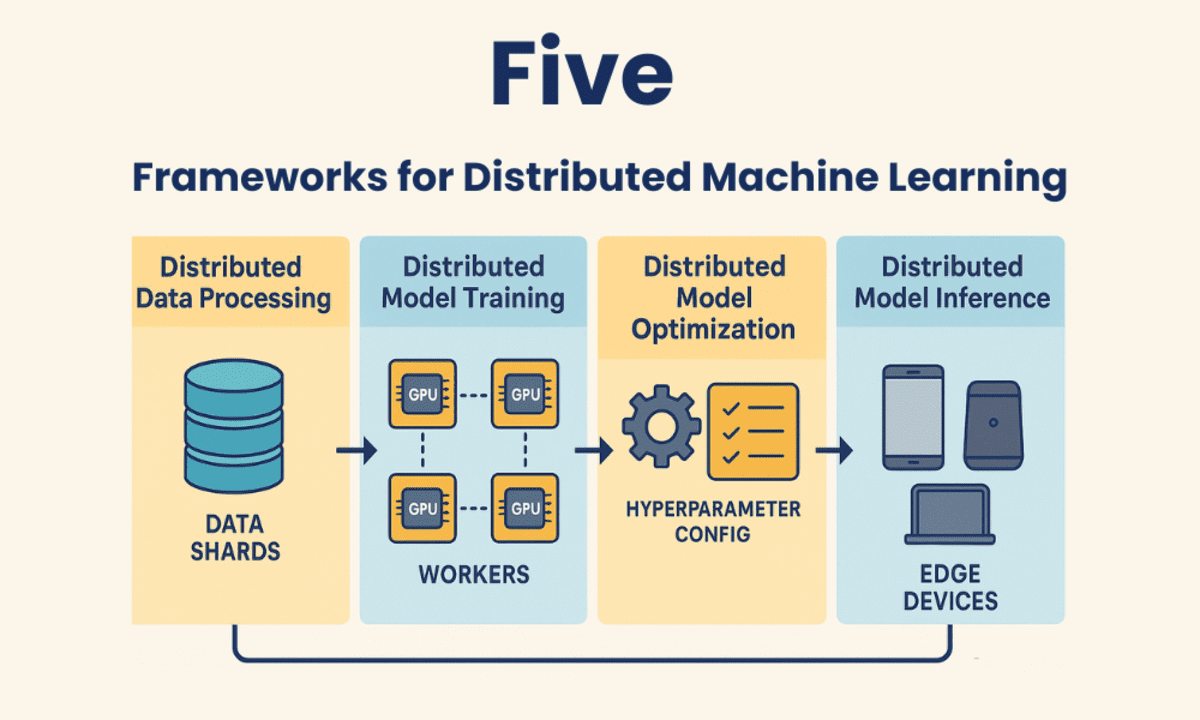
Let’s dive into the five most popular distributed machine learning frameworks that help us scale up machine learning processes. Each framework comes with its unique solutions tailored to specific project requirements.
If you’re working with large-scale structured or semi-structured data and need a comprehensive framework for both data processing and machine learning, Spark is a brilliant choice.
Dask is an ideal choice for Python developers who want a flexible, lightweight framework to boost their existing workflows. Its seamless integration with Python libraries makes it easy for teams already familiar with the Python ecosystem.
TensorFlow Distributed is a top pick for teams already working with TensorFlow or those in search of a highly scalable solution that aligns well with cloud-based machine learning processes.
Dask is a lightweight, Python-native framework for distributed computing. It extends popular Python libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Scikit-learn to handle datasets that are too large for memory, making it perfect for Python developers looking to scale their existing workflows.
Apache Spark is a mature, open-source distributed computing framework focused on large-scale data processing. It features MLlib, a library that supports distributed machine learning algorithms and workflows.
Picture by Author
The great thing about distributed machine learning (DML) frameworks is they let you train machine learning models on multiple machines (using CPUs, GPUs, or TPUs), which can really cut down on training time and handle large and complicated workloads that wouldn’t otherwise fit in memory. On top of that, these frameworks allow you to work with datasets, fine-tune models, and even deploy them using distributed computing resources.
It’s a great fit for teams already using PyTorch for model development who want to level up their workflows. Converting your training script to utilize multiple GPUs is a breeze with just a few lines of code.
PyTorch is a favorite among machine learning experts due to its dynamic computation graph, user-friendliness, and modular design. PyTorch Distributed is part of the framework and helps scale deep learning models across multiple GPUs and nodes.
I’ve had experience with almost all distributed computing frameworks mentioned here, but I mainly stick with PyTorch and TensorFlow for deep learning tasks. These frameworks make it super easy to scale model training across multiple GPUs with minimal code.
Abid Ali Awan (@1abidaliawan) is a certified data scientist professional who absolutely loves creating machine learning models. Currently, he’s diving into content creation and writing technical blogs on machine learning and data science technologies. Abid holds a Master’s degree in technology management and a bachelor’s degree in telecommunication engineering. His goal is to build an AI product using a graph neural network to support students struggling with mental health issues.
Ray is a versatile framework for distributed computing, designed to optimize machine learning and AI tasks. It simplifies the creation of distributed machine learning pipelines by providing specialized libraries for training, fine-tuning, and deploying models.
Ray is a fantastic option for AI and machine learning developers seeking a modern framework that supports distributed computing across all stages, from data preprocessing and model training to fine-tuning and deployment.